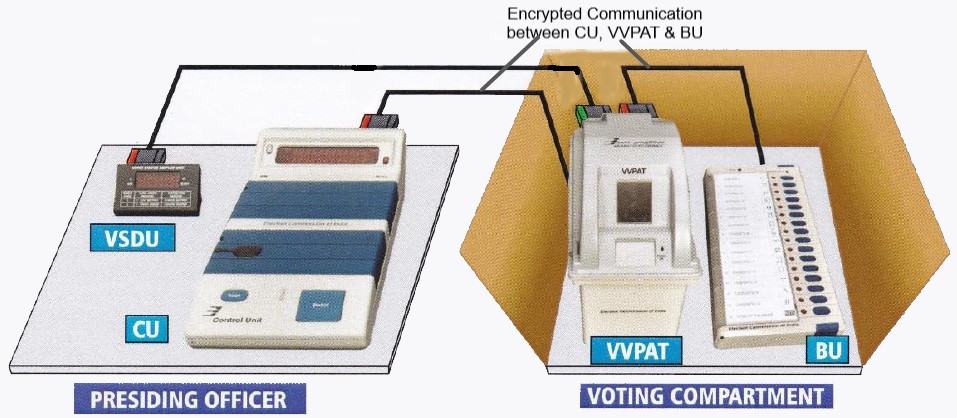
Electronic Voting Machines (EVMs) are the backbone of India’s electoral process conducted by Election Commission of India (ECI).
History, design, and significance of EVMs
- Introduction and Evolution:
- EVMs were introduced as an alternative to paper ballots. The ballot papers were prone to fraudulent voting and booth capturing.
- Developed and tested by the state-owned Electronics Corporation of India (ECIL) and Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL) in the 1990s.
- EVMs were gradually phased into Indian elections between 1998 and 2001.
- Design and Technology:
- EVMs are standalone machines with secure manufacturing practices.
- They are self-contained, battery-powered, and lack any networking capability.
- EVMs do not have wireless or wired internet components, ensuring tamper-proof operation.
- The M3 version includes the Voter-Verified Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT) system.
- Functionality and Security Features:
- EVMs electronically limit the rate of casting votes to five per minute.
- A security “lock-close” feature ensures integrity.
- An electronic database stores “voting signatures and thumb impressions” to confirm voter identity.
- Advantages:
- Reduced electoral fraud voting and booth capturing.
- Fairer and more competitive elections.
- Voter-Verified Paper Audit Trail (VVPAT):
- VVPAT was introduced after court rulings, to provides transparency.
- It allows voters to verify their vote through a printed paper trail.
- EVMs and VVPATs are now used in every assembly and general election in India.
- Recent Developments:
- In 2019, the Supreme Court ordered the use of VVPAT in every assembly constituency, verifying a small percentage of EVMs before certifying final results.
Q: What does VVPAT stand for in the context of EVMs?
A) Verified Voter Paper Authentication Technology
B) Voter-Verified Polling Accuracy Tracker
C) Voter-Verified Paper Audit Trail
D) Verified Voting Process and Accountability Tool
Ans : C) Voter-Verified Paper Audit Trail
Q: Which organization developed and tested EVMs in India during the 1990s?
A) Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) and Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL)
B) Electronics Corporation of India(ECIL) and Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL)
C) Indian Institute of Technology (IIT) and Electronics Corporation of India(ECIL)
D) Bharat Heavy Electricals Limited (BHEL) and Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO)
Ans : B) Electronics Corporation of India(ECIL) and Bharat Electronics Ltd (BEL)