Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla Becomes First Indian to Visit ISS on Axiom-4 Mission
The Axiom-4 (Ax-4) mission, carrying Indian astronaut Group Captain Shubhanshu Shukla, is scheduled to dock with the International Space Station (ISS) today at 4:30 PM IST, according to ISRO.
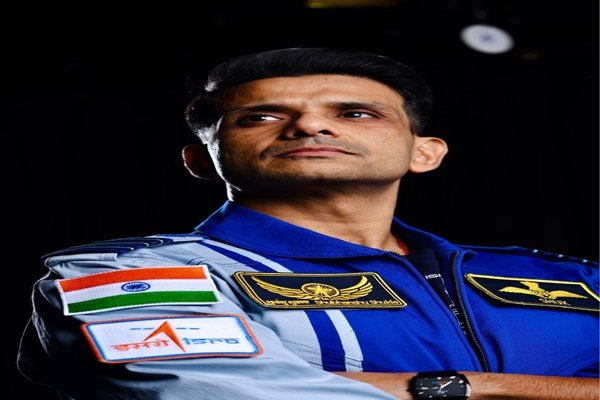
With this mission, Shukla becomes the first Indian to visit NASA’s orbiting laboratory ISS and the second Indian in history to travel to space, following Rakesh Sharma who flew in 1984 aboard a Russian Soyuz spacecraft.
The Axiom-4 crew launched from NASA’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida at 12:01 PM IST on 25 June 2025, and includes:
- Shubhanshu Shukla (India)
- Peggy Whitson (USA, former NASA astronaut)
- Slawosz Uznanski-Wisniewski (Poland)
- Tibor Kapu (Hungary)
Shukla, born on 10 October 1985 in Lucknow, joined the Indian Air Force in 2006 as a fighter pilot and has over 2,000 hours of flying experience on aircraft such as MiGs, Sukhois, Dorniers, Jaguars, and Hawks.
Prime Minister Narendra Modi praised the mission, saying Shukla carries the hopes of 1.4 billion Indians. In Lucknow, his parents watched the launch with local students amid celebrations.
While on the two-week mission aboard the ISS, the Ax-4 crew will conduct 60 scientific experiments, including seven from India. Key experiments by ISRO include studying the effects of microgravity on biology and six varieties of crop seeds.
Shukla’s flight marks India’s return to space after 41 years, and highlights the growing international collaboration in human spaceflight.