Cabinet Approves Changes to FDI Policy for Investments from Neighbouring Countries
The Union Cabinet of India, chaired by Narendra Modi, approved amendments to India’s Foreign Direct Investment (FDI) policy on 10 March 2026 for investments from countries sharing a land border with India.
The revised policy introduces clearer rules for determining “beneficial ownership” and sets a 60-day timeline for approving investment proposals in key manufacturing sectors such as electronic components, capital goods, and solar manufacturing.
Under the new guidelines, non-controlling investments of up to 10% beneficial ownership by entities from land-bordering countries can now be allowed through the automatic route, subject to sectoral limits and reporting to the Department for Promotion of Industry and Internal Trade (DPIIT). However, majority ownership and control must remain with Indian citizens or Indian-owned companies.
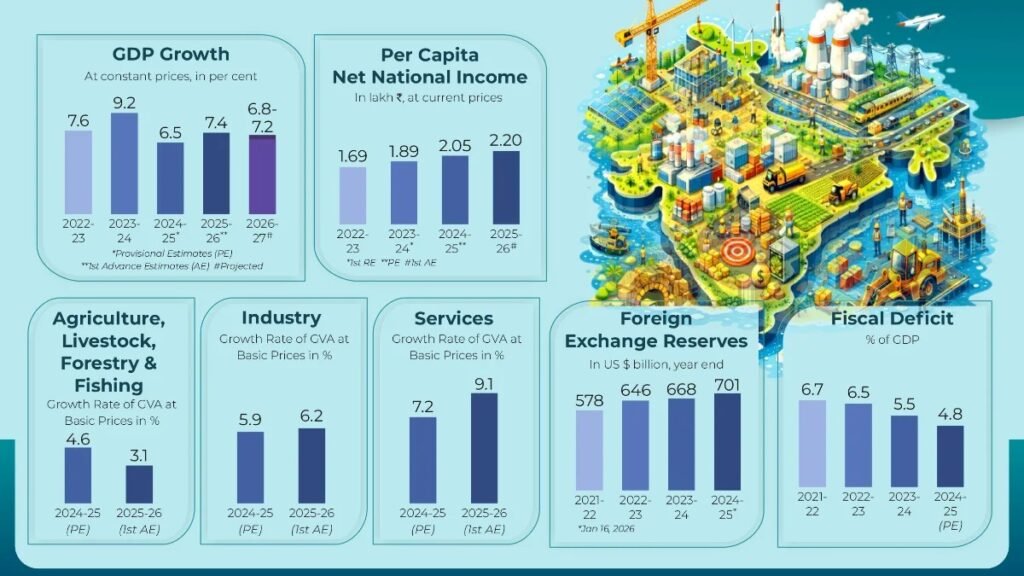
The reform modifies the earlier restrictions introduced through Press Note 3 (2020), which required government approval for all investments from neighboring countries. The new changes aim to improve ease of doing business, attract more FDI, promote technology transfer, and strengthen India’s manufacturing sector under the Atmanirbhar Bharat initiative.