DRDO Successfully Tests Gaganyaan Drogue Parachute
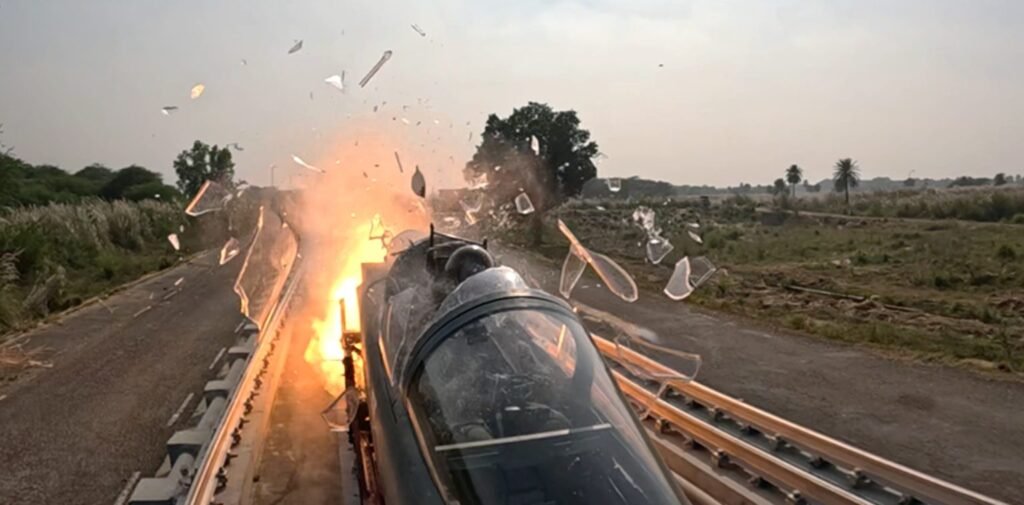
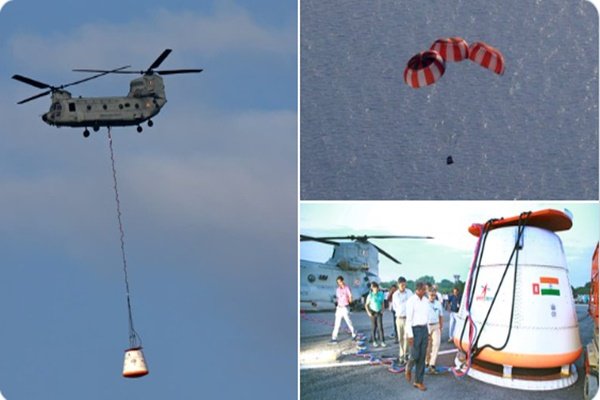
India’s human spaceflight programme, Gaganyaan, achieved a significant milestone with the successful qualification-level load test of its drogue parachute system. The test was conducted by the Defence Research and Development Organisation (DRDO) at the Rail Track Rocket Sled (RTRS) facility of the Terminal Ballistics Research Laboratory (TBRL) in Chandigarh on 18 February 2026.
Key Highlights
- The drogue parachute is a critical component of the crew module’s deceleration system, designed to stabilize and slow down the spacecraft before the deployment of the main parachutes.
- The qualification-level load test validated the parachute’s strength, reliability, and performance under extreme aerodynamic conditions.
- The Ministry of Defence emphasized that the RTRS facility is a specialized dynamic test center extensively used for high-speed aerodynamic and ballistic evaluations.
- The successful trial demonstrates India’s growing expertise in designing and manufacturing high-strength ribbon parachutes, a technology crucial for astronaut safety during re-entry and landing.
- The test was jointly overseen by teams from DRDO and ISRO, marking another step forward in ensuring the safety and success of India’s first human spaceflight mission.