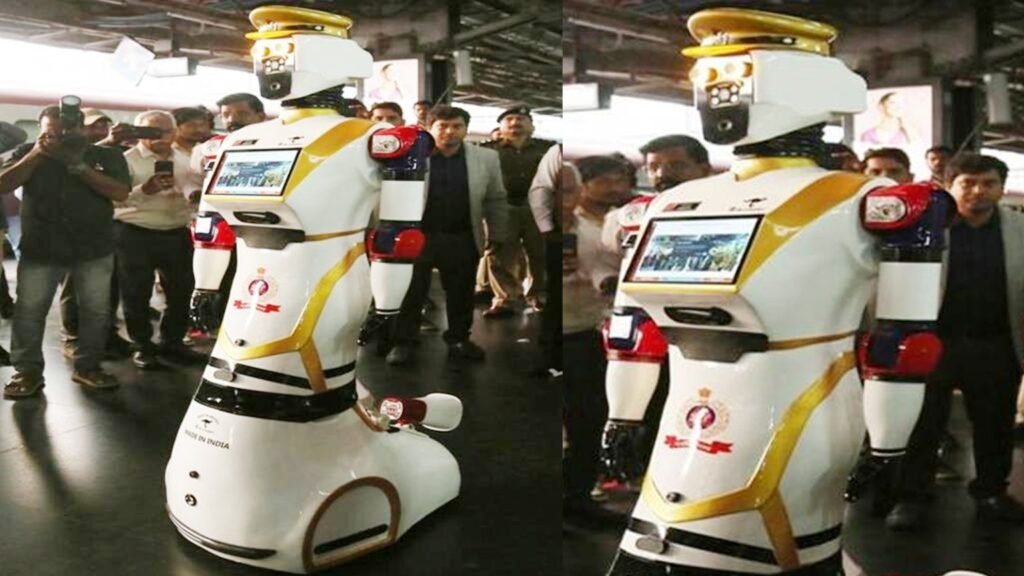
Indian Railways has deployed its first humanoid robot, ASC ARJUN, at Visakhapatnam Railway Station to strengthen passenger safety, security, and service delivery. The robot will function alongside Railway Protection Force (RPF) personnel, especially during periods of heavy passenger movement, reflecting Indian Railways’ commitment to adopting emerging technologies for improved operational efficiency and public convenience.
The robot was unveiled by Inspector General (RPF) Alok Bohra and Divisional Railway Manager Lalit Bohra, in the presence of senior RPF officials. Developed entirely in Visakhapatnam using indigenous technology, ASC ARJUN is the outcome of over a year of work by a dedicated technical team, highlighting Indian Railways’ growing capability to integrate advanced systems into routine operations.
ASC ARJUN is equipped with a Face Recognition System (FRS) for intrusion detection, AI-based crowd monitoring, and real-time alert generation for RPF control rooms. It can make automated public announcements in English, Hindi, and Telugu, enhancing passenger assistance and safety awareness.
With semi-autonomous navigation and obstacle-avoidance, the robot can patrol platforms round the clock, supporting surveillance and optimizing manpower deployment. Additional features include fire and smoke detection systems for emergency response, as well as interactive functions such as greeting passengers with a Namaste, saluting RPF personnel, and providing information through a user interface.
The Ministry of Railways stated that ASC ARJUN’s deployment is part of a broader strategy to leverage technology-driven and indigenously developed innovations to create a safer, more secure, and passenger-friendly railway environment.