56th International Chemistry Olympiad : Indian Team Wins one Gold, Two Silver, and a Bronze
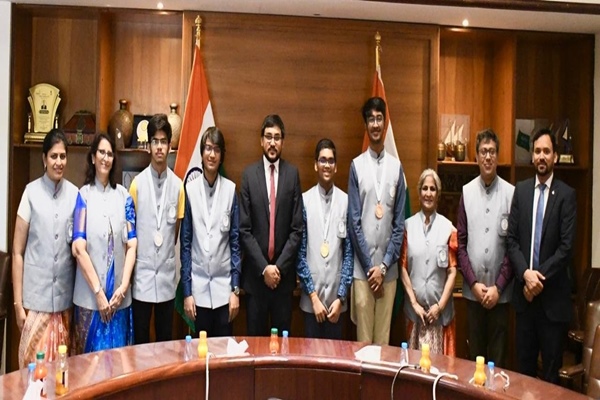
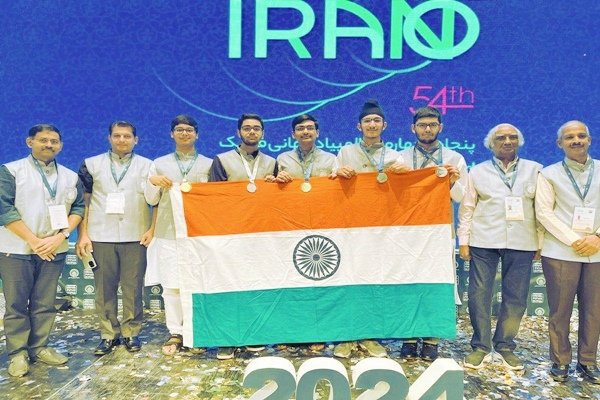
The 56th International Chemistry Olympiad was held in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia from July 21st to 30th, 2024. The Indian team won one Gold, two Silver, and one Bronze medal.
- Devesh Bhaiyya from Jalgaon, Maharashtra won the Gold medal.
- Avanish Bansal from Mumbai and Harshin Posina from Hyderabad won Silver medals.
- Kashyap Khandelwal from Mumbai won the Bronze medal.
Prof. Gulshanara Shaikh and Dr. Shraddha Tiwari guided the Indian team.
327 students from 94 countries participated in the Olympiad.
Q.: Who won the Gold medal for India at the 56th International Chemistry Olympiad held in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia from July 21st to 30th, 2024?
(A) Avanish Bansal
(B) Harshin Posina
(C) Kashyap Khandelwal
(D) Devesh Bhaiyya
Ans : (D) Devesh Bhaiyya
Devesh Bhaiyya from Jalgaon, Maharashtra won the Gold medal in the 56th International Chemistry Olympiad held in Riyadh, Saudi Arabia from July 21st to 30th, 2024